Welcome to the world of cohort analysis! In this guide, we’ll embark on an exciting journey into the realm of data-driven insights and user behaviour. Cohort analysis is like a powerful magnifying glass that allows us to zoom in on specific groups of users, uncovering valuable patterns and trends that can shape the future of our businesses.
Understanding user behaviour is key to success in today’s competitive landscape. It’s not just about attracting users; it’s about keeping them engaged and satisfied over the long term. That’s where cohort analysis comes in. By examining how different groups of users behave over time, we can gain profound insights into what drives retention, engagement, and ultimately, growth.
So, whether you’re a seasoned data analyst or a curious entrepreneur looking to better understand your customers, buckle up and get ready to dive deep into the world of cohort analysis. Your journey to unlocking actionable insights starts here!
Table of Contents
What is Cohort Analysis?
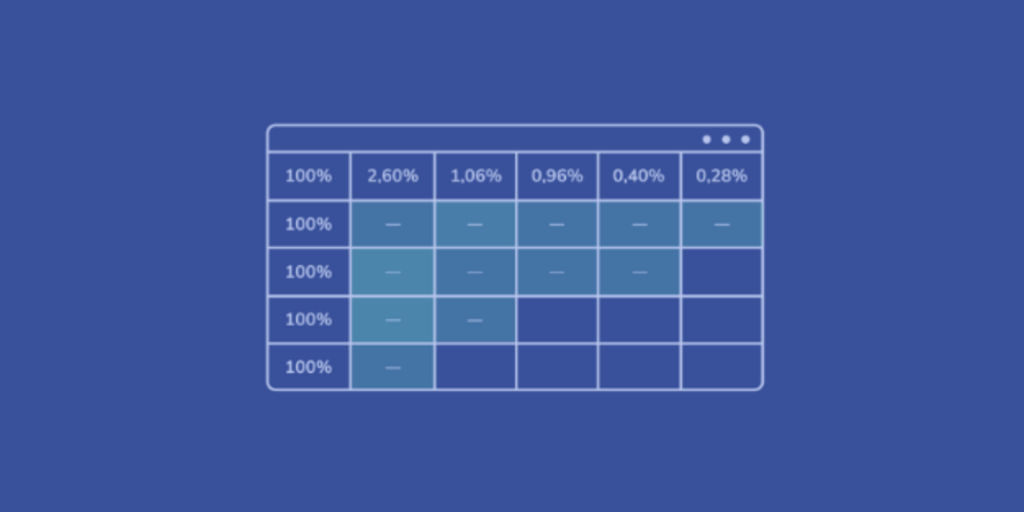
At its core, cohort analysis involves grouping users who share a common characteristic or experience within a defined time period. These groups, known as cohorts, are invaluable lenses through which businesses can analyse user behaviour and track changes over time.
Cohort analysis serves several purposes, all geared towards unravelling the mysteries of user engagement and retention. By comparing the behaviour of different cohorts, businesses can identify trends, patterns, and insights that might otherwise go unnoticed. This granular approach to data analysis enables more informed decision-making, leading to improvements in product development, marketing strategies, and overall user experience.
The benefits of cohort analysis are manifold. Not only does it provide deeper insights into user behaviour, but it also helps businesses identify areas for optimization and growth. By understanding how different cohorts respond to various stimuli, businesses can tailor their efforts to better meet the needs and preferences of their target audience, ultimately driving long-term success and profitability.
Step-by-Step Guide to Conducting Cohort Analysis
1. Define Your Cohorts
Defining your cohorts is the foundational step in cohort analysis. It involves identifying the common characteristic or event that distinguishes one group of users from another. Cohorts can be defined based on various criteria such as sign-up date, acquisition channel, and geographic location. The chosen cohort definition should align with your analysis goals and the specific questions you seek to answer. Clear and well-defined cohorts enable meaningful comparisons and insights into how different groups of users behave over time.
2. Gather Data
Gathering data is the next crucial step in cohort analysis. It involves collecting relevant information for each user within the defined cohorts. This includes capturing data points such as sign-up dates, acquisition sources, user activities (e.g., interactions, purchases), and any additional demographic or behavioural data. Depending on the scope of your analysis, data may be sourced from various sources such as customer relationship management (CRM) systems, web analytics platforms, or transactional databases.
3. Clean and Prepare Data
Cleaning and preparing data is essential for ensuring its accuracy and reliability in cohort analysis. This involves identifying and addressing inconsistencies, errors, and missing values within the dataset. Common tasks include removing duplicates, standardizing formats, and correcting discrepancies. By meticulously cleaning and preparing the data, analysts can mitigate the risk of bias and distortion, thus facilitating more accurate and meaningful insights from the cohort analysis process.
4. Calculate Cohort Metrics
Calculating cohort metrics involves computing key performance indicators (KPIs) for each cohort to evaluate user behaviour over time. Common cohort metrics include retention rate, conversion rate, average revenue per user (ARPU), and others tailored to specific analysis goals. By quantifying these metrics, analysts gain valuable insights into user engagement, retention, and revenue generation patterns, enabling informed decision-making and strategic optimization efforts to enhance overall business performance.
5. Create Cohort Analysis Visualizations
Creating cohort analysis visualizations transforms raw data into actionable insights. Utilizing tools such as Excel, Google Sheets, or specialized analytics platforms, analysts can generate visual representations of cohort behaviour over time. Examples include cohort retention curves, stacked bar charts, and heat maps. These visualizations allow for easy comparison between cohorts and identification of trends and patterns. By presenting data visually, stakeholders can quickly grasp complex information and make informed decisions, driving strategic initiatives to improve user engagement, retention, and overall business success.
6. Interpret Results
Interpreting results is pre-penultimate and a critical phase of cohort analysis, where analysts delve into the visualizations and metrics to extract meaningful insights. This involves examining trends, identifying patterns, and understanding the implications of the data. Analysts may explore factors driving differences between cohorts and assess the effectiveness of various strategies or interventions. By scrutinizing the findings in context with business objectives, analysts can derive actionable insights that inform decision-making, optimize resource allocation, and drive sustainable growth. Effective interpretation transforms raw data into actionable intelligence, guiding strategic initiatives and driving business success.
7. Draw Conclusions and Insights
Drawing conclusions and insights from cohort analysis involves synthesizing the findings and translating them into actionable recommendations. Analysts assess the implications of the data, considering factors such as user behaviour trends, cohort performance variations, and the impact of strategic initiatives. Key insights may include identifying high-performing cohorts, pinpointing areas for improvement, and uncovering opportunities for optimization. These insights empower decision-makers to refine marketing strategies, enhance product features, and personalize user experiences, ultimately driving long-term growth and success. Effective conclusion drawing from cohort analysis fosters data-driven decision-making and accelerates organizational agility.
8. Apply Insights to Business Decisions:
Applying insights from cohort analysis to business decisions is a crucial step in leveraging data-driven strategies for success. Decision-makers use the derived insights to inform and guide various aspects of the business, including marketing campaigns, product development, and customer engagement initiatives. For instance, insights may lead to targeted marketing efforts towards high-performing cohorts or the optimization of product features based on user behaviour patterns. By aligning business decisions with data-driven insights, organizations can enhance operational efficiency, drive revenue growth, and foster stronger relationships with their customers, ultimately gaining a competitive edge in the market.
9. Monitor and Iterate:
Monitoring and iteration are integral components of the cohort analysis process, ensuring continuous improvement and adaptation to changing circumstances. After implementing decisions based on cohort analysis insights, it’s essential to monitor their impact on key metrics and user behaviour over time. This ongoing monitoring allows organizations to assess the effectiveness of their strategies and initiatives and identify any unexpected outcomes or trends.
By embracing a cycle of monitoring and iteration, organizations can maintain agility and responsiveness, continuously improving their strategies and staying ahead of the curve in a dynamic business environment.
Best Practices for Effective Cohort Analysis
Consistency in Cohort Definition: Maintain consistency in defining cohorts throughout the analysis to ensure meaningful comparisons over time. Clearly define the criteria for grouping users, such as sign-up date or acquisition channel, and adhere to these definitions consistently across all analyses.
Granularity of Analysis: Consider the level of detail needed for your analysis and choose an appropriate level of granularity. While broad cohorts provide an overview of trends, more granular cohorts offer deeper insights into specific user segments or behaviours. Tailor the granularity of your analysis goals and the questions you seek to answer.
Segmentation for Deeper Insights: Segment cohorts based on relevant variables such as demographics, behaviour, or usage patterns to uncover hidden trends and patterns. By analysing subgroups within cohorts, you can identify nuances and opportunities for targeted interventions or optimizations.
Continual Monitoring and Iteration: Cohort analysis is not a one-time activity but an iterative process. Continuously monitor key metrics and user behaviour and iterate on your analysis and strategies based on new insights and changing conditions. This iterative approach ensures that your analysis remains relevant and actionable in driving ongoing improvements and optimizations.
By following these best practices, organizations can conduct more effective cohort analysis, unlocking valuable insights into user behaviour and driving informed decision-making for sustainable growth and success.
Challenges and Pitfalls of Cohort Analysis
- Data Quality Issues: Cohort analysis relies heavily on the accuracy and completeness of data. Inaccurate or incomplete data can skew analysis results and lead to erroneous conclusions. Ensuring data quality through thorough cleaning and validation processes is essential to mitigate this challenge.
- Selection Bias: Cohort analysis may suffer from selection bias if cohorts are not appropriately defined or if certain user groups are overrepresented or underrepresented. This bias can distort analysis results and undermine the validity of insights derived from cohort analysis.
- Interpretation Challenges: Cohort analysis results can be complex and multifaceted, requiring careful interpretation to extract meaningful insights. Misinterpretation of data or overlooking subtle trends can lead to misguided decisions and ineffective strategies.
By addressing data quality issues, ensuring cohort definitions are consistent and representative, and exercising caution in interpreting results, organizations can maximize the value of cohort analysis and drive more informed decision-making.
Future Trends
Looking ahead, several trends are poised to shape the landscape of cohort analysis. One key trend is the integration of advanced analytics techniques, such as machine learning and predictive modelling into cohort analysis methodologies. This integration will enable more sophisticated segmentation and personalized insights from cohort analysis. Another emerging trend is the emphasis on real-time cohort analysis, enabled by advancements in data processing technologies and analytics platforms. Real-time cohort analysis allows organizations to react swiftly to changing user behaviour and market dynamics, enabling more agile decision-making and proactive interventions.
Additionally, as privacy regulations evolve and consumer expectations around data protection increase, there will be a growing focus on ethical data collection and usage practices in cohort analysis. Businesses will need to prioritize transparency, consent, and data security to maintain trust and compliance while extracting valuable insights from cohort analysis.
Conclusion
Cohort analysis stands as a powerful tool for businesses seeking to understand user behaviour, drive informed decision-making, and achieve sustainable growth. Through the systematic grouping of users and analysis of their behaviour over time, organizations can uncover valuable insights into retention patterns, conversion rates, and revenue generation. By leveraging these insights, businesses can optimize marketing strategies, refine product offerings, and enhance the overall user experience, ultimately leading to increased customer satisfaction and long-term profitability.
However, cohort analysis is not without its challenges, including data quality issues, selection bias, and interpretation complexities. Overcoming these challenges requires careful attention to data integrity, consistent cohort definitions, and diligent interpretation of results.
As businesses embrace the iterative nature of cohort analysis, continually monitoring and iterating based on new insights, they position themselves to adapt to evolving market conditions and stay ahead of the competition. By incorporating cohort analysis into their decision-making processes, organizations can unlock the full potential of their data and drive meaningful improvements that propel them towards success in today’s dynamic business landscape.






